
Nuclear energy’s environmental impacts can be more closely monitored than the impacts of other energy sources, because it’s easy to measure radioactivity at orders of magnitude below the levels hazardous to human health. With energy sources such as coal and gas, it is not possible to dispose of all waste - there is simply too much of it. Relative to the price of electricity, radioactive waste from power plants can be disposed of in geologic repositories at low cost currently, this technology is used to dispose of hazardous chemical waste in Europe, and defense-related transuranic radioactive waste at the US Energy Department’s Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico. The high energy density of uranium not only makes it an affordable option for countries seeking energy independence, but also produces relatively small quantities of waste. Nuclear power in these countries is part of a larger policy that includes high-speed electric trains, efficient vehicles, and other measures to reduce oil and gas consumption.Įnvironmental impacts. France and Japan chose nuclear energy, a difficult technology, not because it was popular but because the alternatives were worse. Similarly, the French nuclear power program is a consequence of the Algerian war, after which the French concluded that only fools would bet their future on Mideast oil. Why is this relevant to nuclear energy? Japan’s nuclear power program can be traced to World War II, after which the Japanese concluded that war was not the right route to energy security. By comparison, Exxon Mobil and BP have combined reserves of less than 28 billion barrels. These reserves are controlled by national oil companies where price and availability are political decisions. US military forces are in the Middle East because Iran and Saudi Arabia each have the equivalent of about 300 billion barrels of recoverable oil and gas Iraq has about 140 billion barrels and Qatar has 180 billion barrels. US alliances with other Arab monarchs, and with Saddam Hussein of Iraq, have had similarly troubled outcomes. In 1979, Iranian anger with the Shah and his foreign backers fueled the Iranian Revolution and the country’s anti-American sentiments. The United States and Britain reacted by organizing a military coup, overthrowing the Iranian democracy, and establishing a monarchy.
#NUCLEAR ENERGY FISSION SERIES#
In 1953 America was drawn into the Middle East when the democratically elected government of Iran responded to a series of oil-company scandals by nationalizing all foreign oil holdings. To prevent that, Japan launched its preemptive attack on Pearl Harbor, precipitating the US entry into World War II. Japan was short on oil and concluded it had to take over Asian oil fields, but feared the US might block its actions. The newly formed state was strategically located halfway between British India and the British Suez Canal.Īmerica’s introduction to energy security came on December 7, 1941, when the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor. But the British Empire had very little oil, so the British Indian Army invaded the northern Persian Gulf and in 1920 carved Iraq out of the Ottoman Empire. During World War I, the British fleet converted from coal to oil. Throughout the industrial age, nations have waged wars to gain control over energy sources.

That can assure a country’s energy independence, which has major implications for war and peace.įighting over oil. Low fuel costs and high energy density enable a country to affordably stockpile a couple years’ worth of nuclear fuel in a space no larger than a small warehouse.
That makes the cost of uranium fuel only two to four percent of the final cost of the electricity.

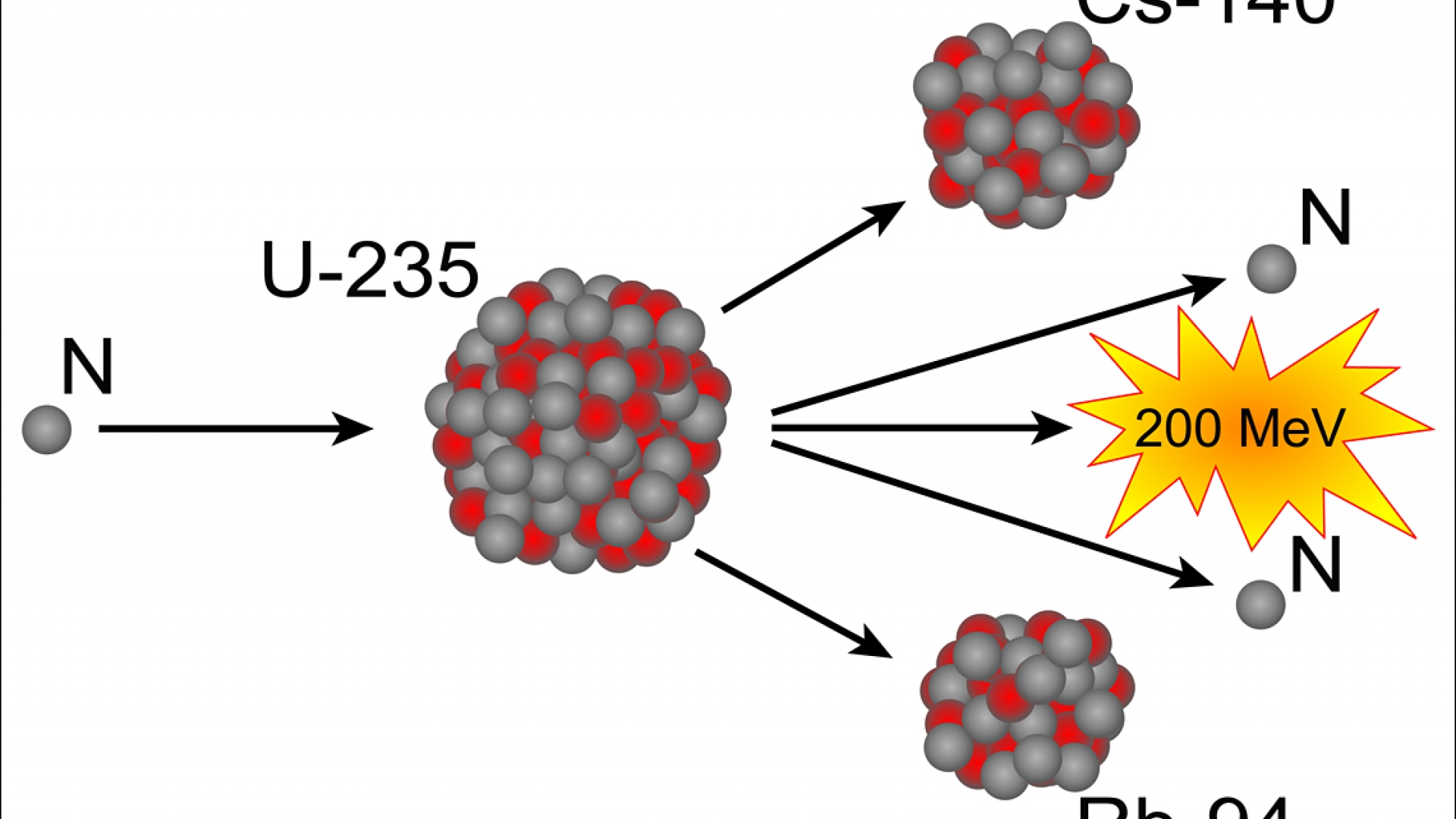
Only 200 tons of milled uranium are needed to fuel a 1,000-megawatt nuclear reactor for a year. Most of nuclear energy’s advantages (such as its relatively small waste volumes) and disadvantages (such as its potential use in nuclear weapons) are a consequence of this characteristic. Coal is abundant but massive quantities of materials must be processed, resulting in large-scale land disturbances and climate change.įor nuclear energy, its most unique characteristic is the massive energy output embodied in each kilogram of uranium fuel-nearly a million times the energy density of fossil fuels. Oil and gas are convenient and easily stored but are concentrated in limited locations, particularly in the Persian Gulf. Renewable energy sources, such as wind turbines and solar panels, do not emit greenhouse gases but produce power intermittently and require large areas of land. For nuclear energy, its most unique characteristic is the massive energy output embodied in each kilogram of uranium fuel-nearly a million times the energy density of fossil fuels.Įvery energy source has unique characteristics that deserve careful consideration and comparison.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
